The DRC’s Demographic Trends – Powerhouse of Central Africa
Demographic Engine
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has one of the world’s fastest-growing populations. The UN puts the 2025 population at ~112.8 million, with an unusually young age structure: roughly 46% are under 15, and population would double in ~22 years if current growth persisted. The median age is about 15–16 years—among the world’s lowest. (United Nations Population Fund, DataReportal – Global Digital Insights)
Fertility remains high by global standards—nearly six births per woman on UN measures—which, combined with improving survival and urbanization, will keep the youth bulge large for decades. (UN WPP 2024 cites the DRC among the highest-fertility countries.) (World Population Prospects, World Bank Open Data)
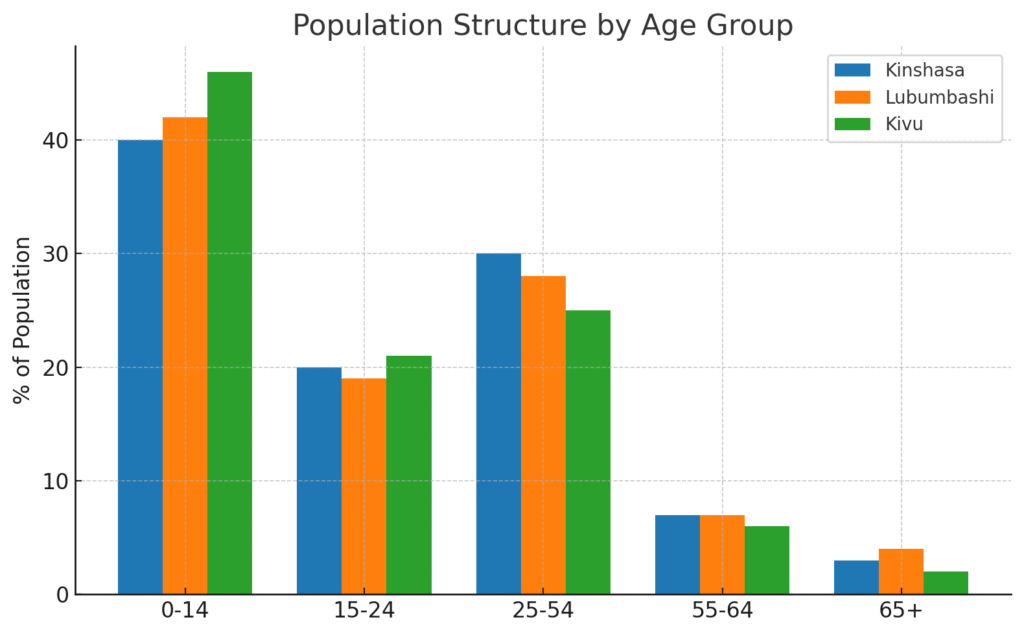
Urbanization: where the demand concentrates
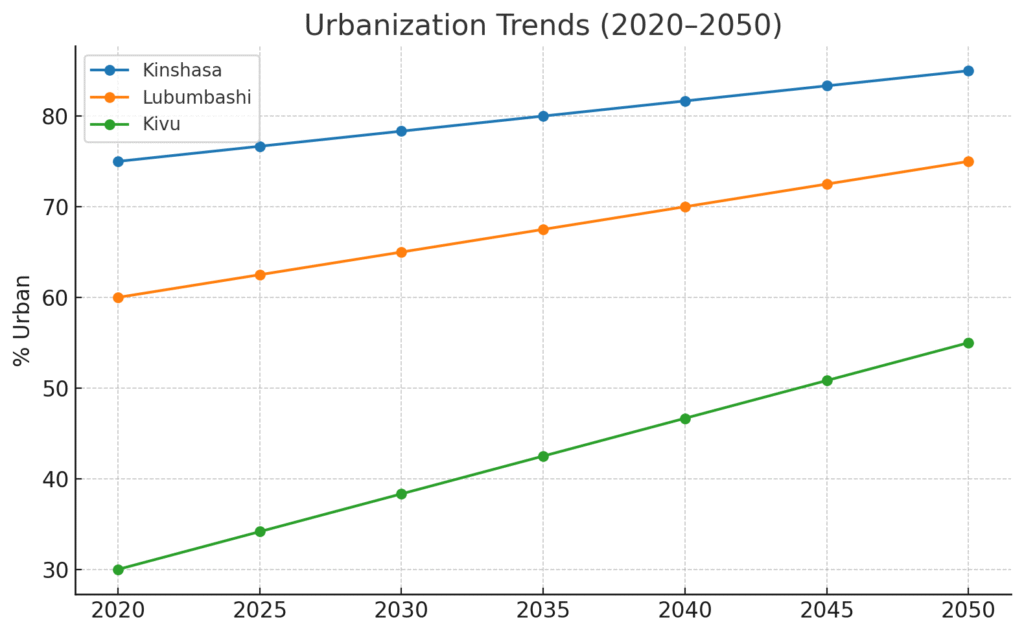
Urbanization is both rapid and durable. Around 48% of Congolese lived in cities at the start of 2024, and multiple UN/UN-Habitat briefs project a majority-urban DRC by mid-century—~60% urban by 2050 with a national population near 145 million. Kinshasa is already a megacity (~18 Million) and is frequently cited as potentially the continent’s largest in the 2030s, concentrating purchasing power in retail, housing, transport, and services. (DataReportal – Global Digital Insights, UN-Habitat, World Bank)
Education & human capital: progress with big gaps
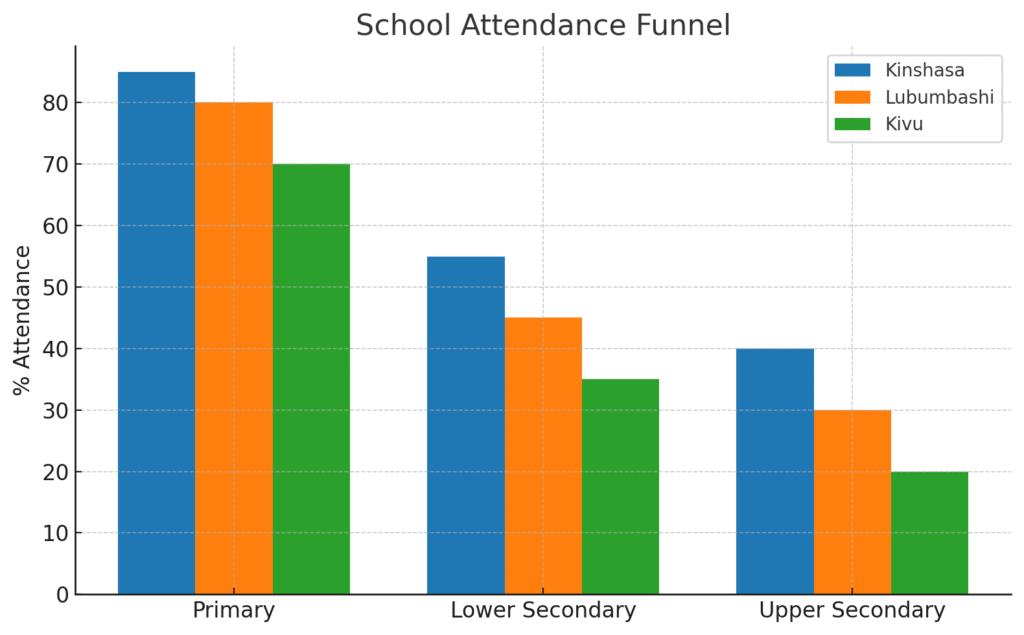
School participation has improved since the mid-2010s, but the pipeline narrows after primary grades. Primary completion reached roughly 79% for girls and 86% for boys (2021) on UNESCO’s UIS data. Yet attendance drops at higher levels: UNICEF reports ~78% primary attendance, ~32% lower-secondary, and ~34% upper-secondary (latest country dashboard). Adult literacy has trended upward to about 80% by 2022 on World Bank/UNESCO series. The picture is progress—but with sharp transition losses at the secondary stage that matter for tomorrow’s workforce quality and earnings. (iicba.unesco.org, UNICEF DATA, FRED)
Digital rails: the on-ramp to modern consumption
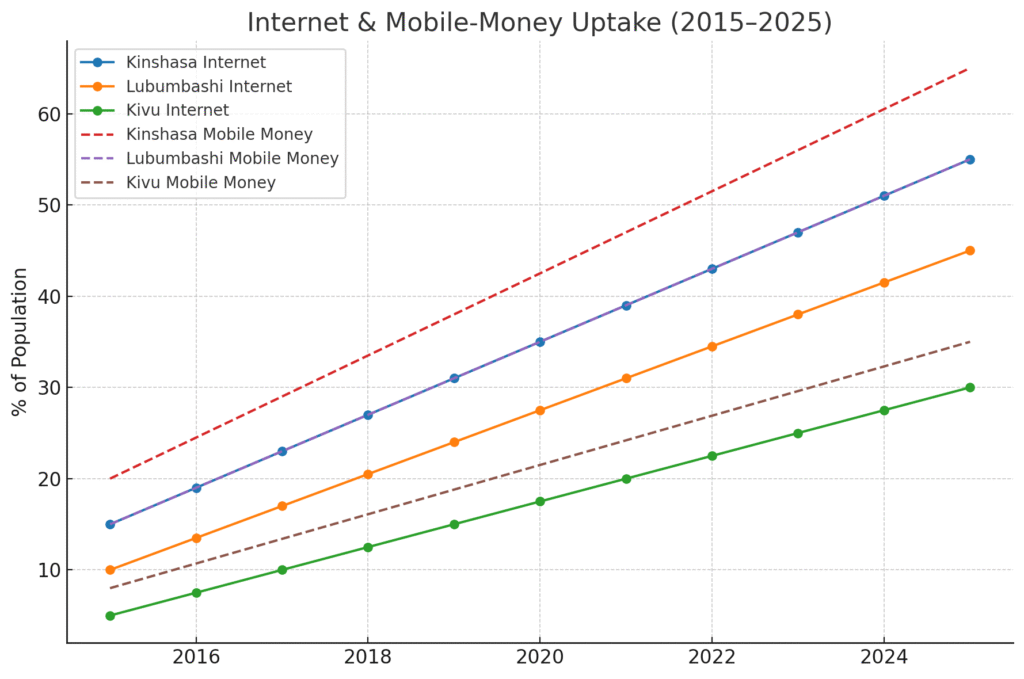
Connectivity is expanding quickly, creating distribution channels for everything from FMCG to finance and media. As of early 2025, the DRC had ~60.3 million active mobile connections and ~34 million internet users (≈31% penetration). Mobile money has surged too: the telecom regulator tallied 23.1 million mobile-money users in Q1 2024 (up from 18.2m a year earlier), deepening the rails for e-commerce, micro-credit, and bill payments. (DataReportal – Global Digital Insights, BANKABLE)
Today’s spending base—and why it can grow
Household consumption already drives the bulk of measured activity—~63% of GDP in 2023—typical of lower-income, commodity-exposed economies where private consumption is the core demand anchor. Still, purchasing power remains extremely constrained: the World Bank estimates ~73.5% of people lived under the $2.15/day extreme-poverty line in 2024, and recurrent conflict and displacement have elevated food insecurity (28 million facing acute hunger in early 2025). These headwinds shape the kinds of products that win—affordable, sachet-sized, and value-first—but also underscore the upside as incomes rise and stability improves. (TheGlobalEconomy.com, World Bank, Reuters)
How the consumer market is likely to evolve (2025–2035)
1) Youth-driven mass market, then a thicker lower-middle. The next decade brings tens of millions of new consumers into cities and into first-time formal markets (banking, ID’d SIMs, formal retail). Expect rising spend per capita first on essentials (staples, hygiene, basic health, telecom/data), then on “next essentials” (education, off-grid energy, transport, housing improvements). Global models (World Data Lab) point to a rising African consumer class; the DRC is a later but large entrant given its scale and urbanization trajectory. (World Economic Forum)
2) Urban retail footprints deepen. More organized retail in Kinshasa/Lubumbashi/Goma, expansion of proximity formats (minimarts, kiosks with digital inventory/float), and FMCG route-to-market modernization (DMS, e-ordering). Logistics players that can bridge port-to-city and city-to-neighborhood gaps will capture outsized value. (Urbanization sources above.) (UN-Habitat)
3) Digital leapfrogging continues. Low-cost Android, expanding 4G (and selective 5G) coverage, plus mobile money rails will push formalization: tuition and utility payments, micro-savings, pay-as-you-go solar, and BNPL-style school/health financing. Fintech/telecom bundles will keep ARPUs rising even at low ticket sizes. (DataReportal – Global Digital Insights, BANKABLE)
4) Education as a growth category. Continued demand for private low-cost schools, tutoring, exam-prep, and TVET—especially ICT, construction, logistics, and basic healthcare—given the big drop-off from primary to secondary and employers’ skill gaps. Providers that prove learning gains at low cost will scale. (UNICEF DATA)
5) Housing & neighborhood services. Urban growth fuels materials (cement, roofing, paints), basic fixtures, and community-level water/sanitation. Bundled services (e.g., solar + appliance financing; water kiosks + digital payments) can address affordability and cash-flow volatility. (Urbanization and poverty sources.) (UN-Habitat, World Bank)
6) Media & entertainment. A super-young, mobile-first audience will keep demand rising for short-form video, streaming bundles, sports, music, and gaming at ultra-low price points (ad-supported, telco-bundled, or community Wi-Fi). (Digital adoption sources.) (DataReportal – Global Digital Insights)
What could accelerate (or slow) the upside
- Stability and macro management. Inflation and conflict are the big swing factors; easing either expands real disposable income and investable footprints. (Reuters)
- Secondary education & skills. Raising transition and completion rates (especially for girls) would compound productivity and lifetime earnings. (UNICEF DATA)
- Infrastructure & regulation. Power, roads, urban planning, and a predictable rule-set (for payments, consumer protection, and competition) are critical to scale distribution and reduce end-user prices. (World Bank/urbanization sources.) (Open Knowledge Repository)
Bottom line
The DRC’s consumer story is scale + youth + urbanization + digital rails—tempered by low incomes and fragility today. Over the next decade, the “mass market” should broaden in the biggest cities first, with steady formalization via mobile money and low-cost connectivity. Companies that design for affordability, solve last-mile logistics, and invest in skills and trust will be best placed to grow with the market as education outcomes and incomes gradually improve. (DataReportal – Global Digital Insights, UNICEF DATA)